Structures
Structures are the arrangement or interrelation of all the parts of a whole, the manner of organization or construction. A structure is one in which the elements are constructed in such a way that the weights, loads, and forces are transferred to the foundations in the most cost-effective manner possible given the structure’s intended function and structure.

Buildings – structures with a roof, windows, and typically more than one story that are used for a variety of activities such as living or entertainment.

Barn house –A barn house is a house that is built to seem like a barn or that has been converted from an actual barn into a living area. The elements of a barn home may differ from one another, but the overall appearance of a barn is kept in the architecture of the house.

Bunk house – An old-fashioned bunkhouse was used to house cowboys on ranches. Everyone shared one huge open room with small mattresses and no privacy.

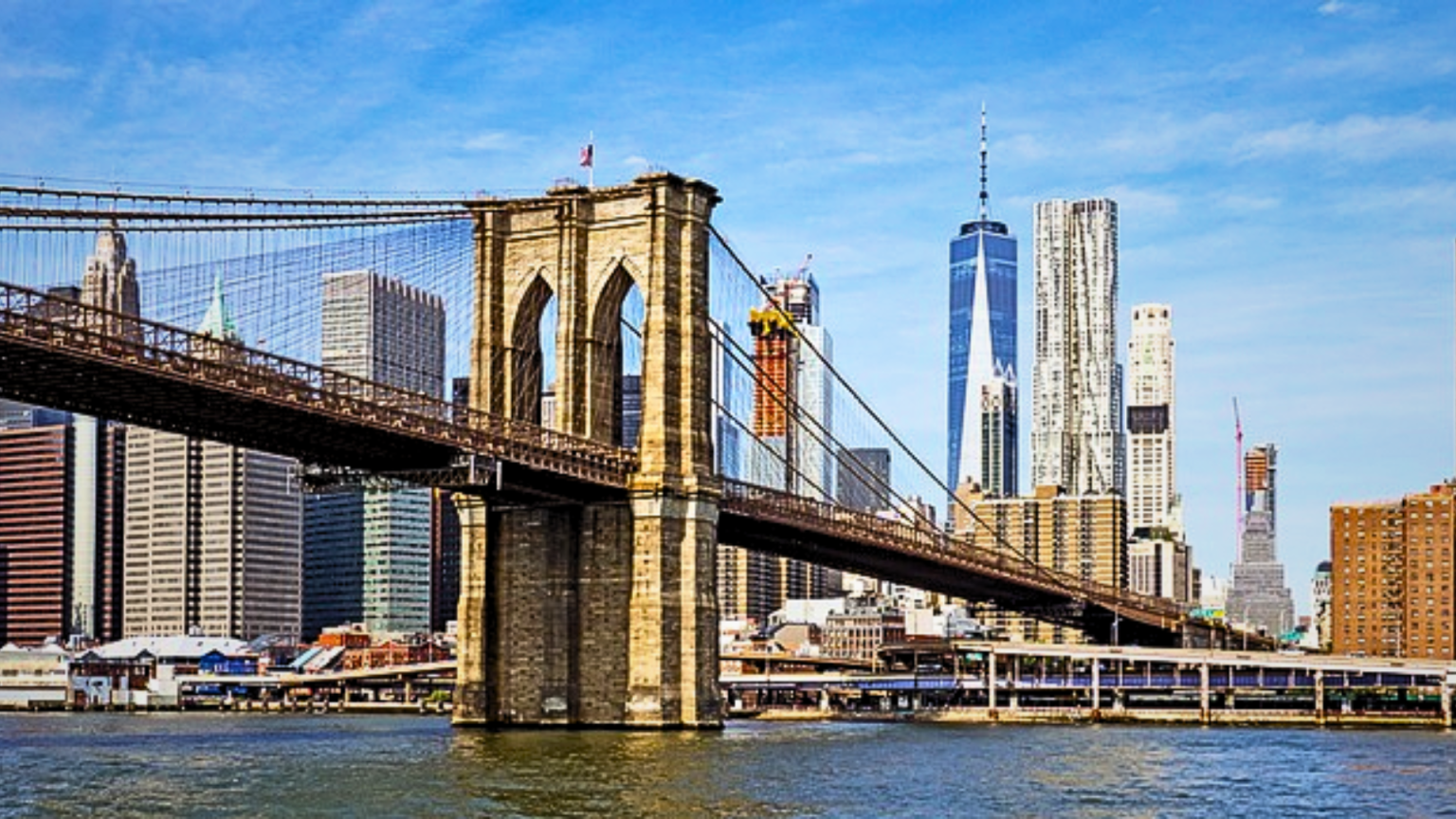
Bridge —Overpasses are bridges that allow people and vehicles to cross a river, road, or train. See Types of Bridge and See Parts of Bridge.

Cantilever – structural piece that extends horizontally and has a single point of support.

Canal-These are canal channels or artificial waterways used for water transportation or to service water transport vehicles. They are artificial rivers that conduct free surface flow under air pressure.

Dam – is a structure constructed to hold water across a stream, river, or estuary. Dams are constructed to supply water for human consumption, irrigation of dry and semiarid regions, or use in industrial operations. See Types of Dam.

Precast concrete – Precast concrete is a type of construction product made by casting concrete in a reusable mold or “form” and curing it in a controlled environment. This provides for full quality control throughout the process, resulting in a consistently long-lasting, high-quality product.

Prestressed Concrete – permits preset engineering stresses to be applied to members to counterbalance loads. Because of this, it has both the great compressive strength of concrete, as well as high tensile strength. See Types of Prestressed Concrete.

Retaining Wall – A retaining wall is a construction that retains or maintains soil in place behind it. Retaining walls can be constructed using a variety of materials, including concrete blocks, poured concrete, treated timbers, pebbles, and boulders. Some are simple to use, while others have a limited lifespan, but all can retain soil. See Types of Retaining Wall.

Road – A road is a long piece of hard ground which is built between two places so that people can drive or ride easily from one place to the other. See Parts of Roadway or Parts of Pavements.

Storey – A storey is one of a building’s multiple levels that is located above or below other levels.

Warehouse -To govern the difference between the flow of products coming in from suppliers or manufacturing centers and the flow of goods leaving the warehouse, we need storage racks, handling equipment, and staff and management resources (goods being sent to production, sales, etc.).

Culvert – structures that allow water to flow through while providing a way to cross a stream or canal. To determine the sort of culver to build, consider factors such as the location’s structural capability, the availability of building materials, and so on. See Types of Culvert.