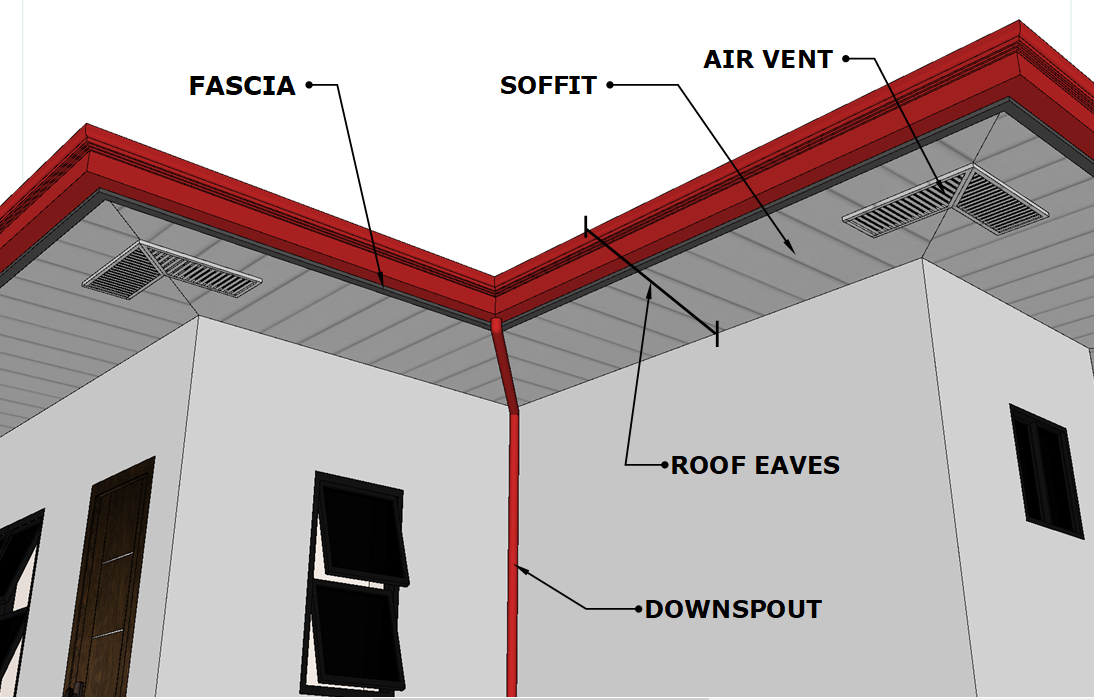
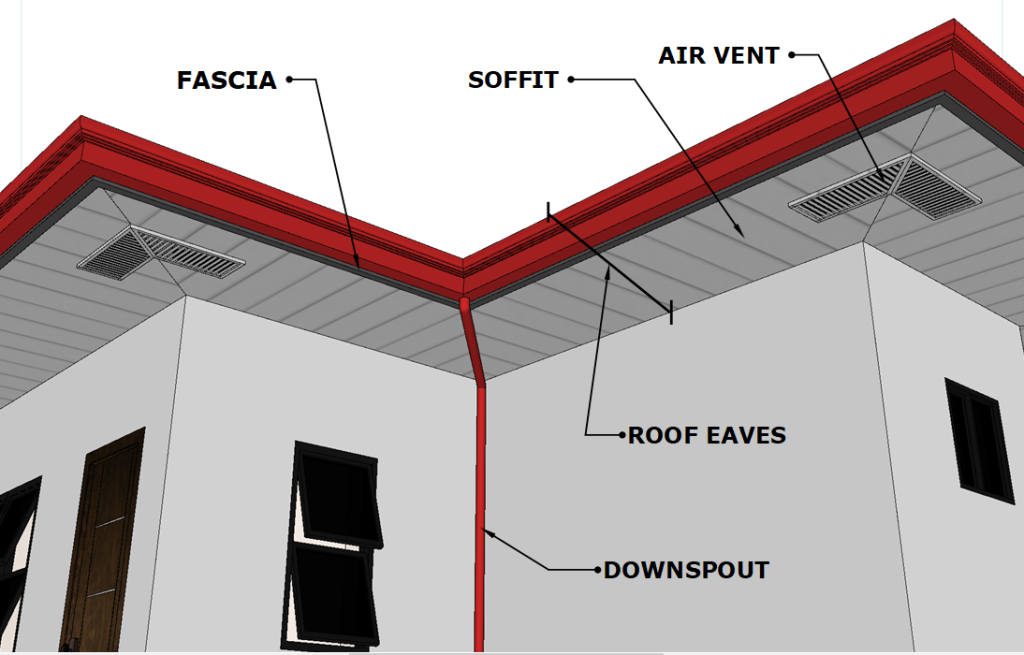
Air Vent- These types of roofs feature an opening that allows air to flow, which may be covered by a grate or grill and may be ducted.
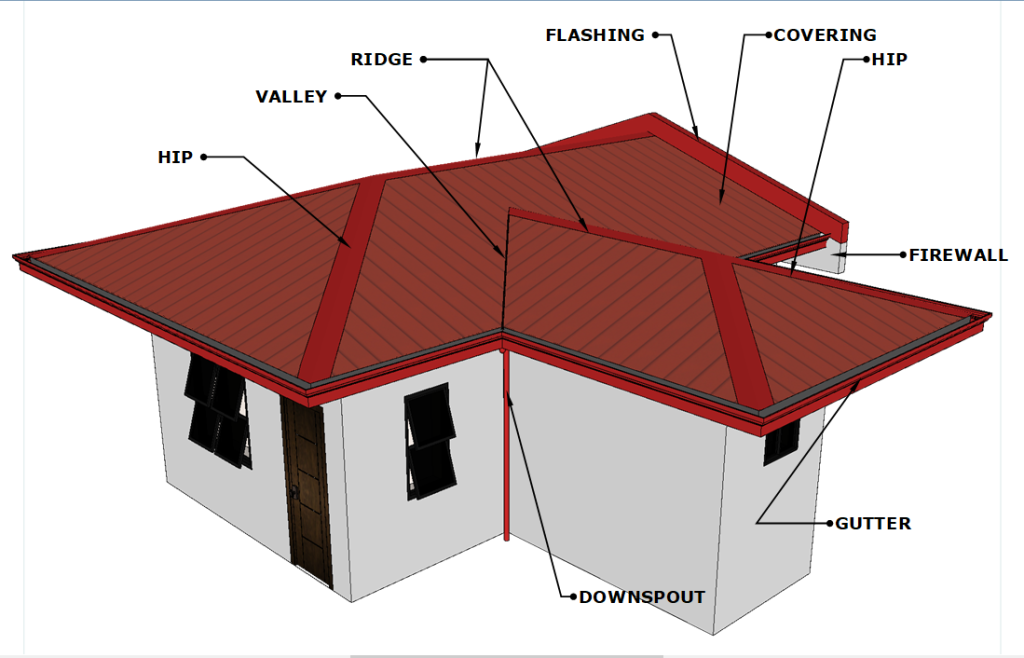
Covering– This is what is fastened to the rafters to keep rain, sun, wind, snow, animal droppings, dust, dirt, and other material out. Popular covering materials include iron sheets, tiles, concrete, and slate.
Downspout– This pipe runs from the roof to the ground vertically. It is linked to the gutter and directs the flow of water to the chosen location. It is constructed of metals such as galvanized steel, plastic, and other materials.
Eaves-In roofing, a roof’s bottom edge (usually overhanging beyond the edge of the house).
Fascia Board– The fascia board is the long, straight plank that spans along the bottom border of the roof. The fascia is directly attached to the lower ends of the roof trusses and serves to support the bottom row of tiles’ lower border. The guttering is supported by the fascia board as well.
Flashing– Flashing is a flat, thin material that is used to keep water out of a roof’s gaps and fissures. It is installed beneath the roof’s shingles and directs water to a different area. Metals including copper, aluminum, stainless steel, and galvanized steel are used to make roof flashing.
Fire Wall– A firewall is a structural construction used to separate transformers, structures, or big buildings to prevent the spread of fire by constructing a wall that spans from the foundation through the roof with a defined fire resistance duration and independent structural stability.
Hip- The hip on a roof is the crossing point of two roof planes that form a sloping ridge extending from the peak to the eave. Hip and ridge shingles are designed specifically for this area of the roof.
Gutter –A gutter is a pipe or trough that runs along the edge of a roof and directs rainwater away from the structure. The gutters on a roof’s role is to keep water from damaging the structure or flooding the area surrounding its base. A gutter directs rainwater away from the house, generally into a drain or rain barrel.
Ridge-The horizontal line that runs along the top of two sloping roof surfaces.
Soffits– The soffit is the portion visible while walking straight up a roof. It is installed between the wall and the fascia or eaves and hides the rafters and ceiling joists.
Valley– This is the intersection of two pitched/sloped roofs that makes a right angle (90 degrees). A valley rafter holds a shallow gutter-like piece below the valley, enabling water and other garbage to cascade down into the gutter.