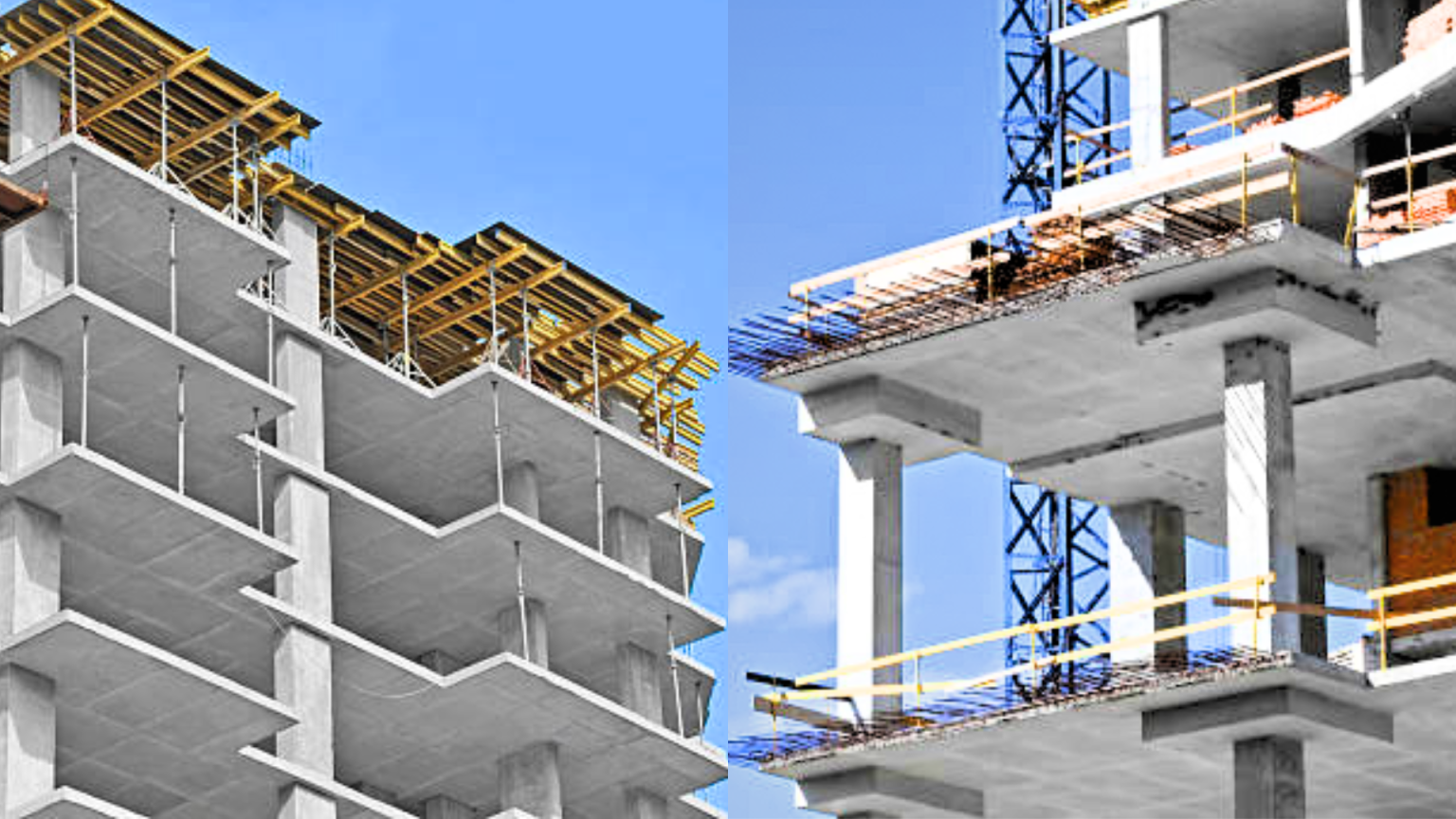

What is Flat Slab?
A flat slab is a type of reinforced concrete slab that does not have beams or girders to support the slab. It consists of a flat, horizontal surface supported directly by columns or walls. In a flat slab system, the load from the slab is transferred directly to the columns or walls through the vertical elements.
The construction of a flat slab involves pouring a continuous slab of concrete over the entire area without any interruptions or beams. The slab is typically thicker near the columns to provide additional strength and stiffness at the points of load transfer. The thickness of the slab gradually decreases towards the middle of the span.
Types of Flat Slab
There are different types of flat slabs that can be used in construction projects, each with its own specific design and construction considerations. Some of the commonly used types of flat slabs include:
- Simple flat slab
- Flat slab with drop panels
- Flat slab with column heads
- Flat slab with both drop panels and column heads
Simple Flat Slab
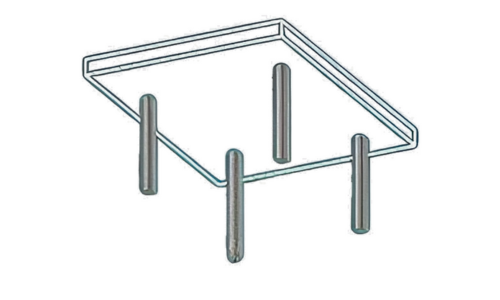
This is the most basic type of flat slab, where the slab is directly supported by columns or walls without the use of drop panels or column heads. The slab thickness is uniform throughout the span.
Flat Slab with Drop Panels
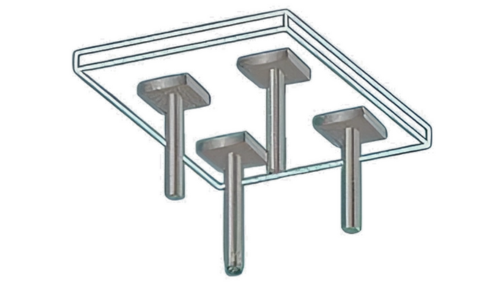
In this type, the slab is thickened around the columns by incorporating drop panels. Drop panels are thickened portions of the slab that help in transferring the load from the slab to the columns more efficiently. They increase the stiffness and load-carrying capacity of the slab.
Flat Slab with Column Heads
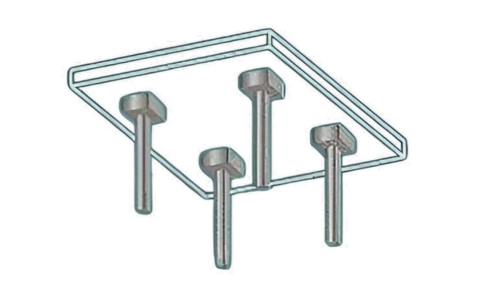
Column heads, also known as column capitals, are enlarged portions at the top of the columns that help in distributing the load from the slab to the columns more evenly. They are often used in conjunction with flat slabs to enhance the load transfer capacity and reduce the slab thickness.
Flat Slab with both drop panel and column heads
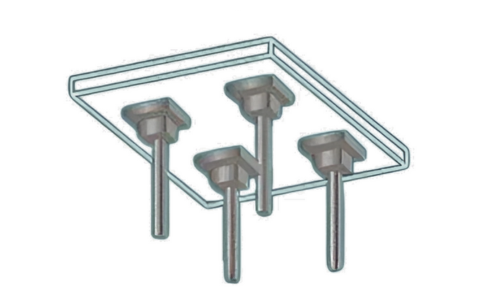
This type combines the use of drop panels and column heads. The drop panels provide additional load transfer capacity around the columns, while the column heads help in distributing the load from the slab to the columns more evenly. This combination enhances the overall performance of the flat slab.
Uses of Column Heads
- It improves the slab’s shear resistance.
- Reducing the effective or clear span lowers the slab’s moment.
Uses of Drop Panels
- It makes the slab more resistant to shear.
- Enhances the slab’s resistance to negative forces.
- It stiffens the slab, reducing deflection.
Advantages of Flat Slab
Flat slabs can be constructed quickly due to their simplified formwork system. The absence of beams and drop panels reduces the complexity of formwork arrangements, resulting in faster construction times and potentially shorter project schedules.
It allow for better quality control during construction. The simplicity of the formwork system and the absence of beams or ribs make it easier to ensure proper concrete placement, reinforcement installation, and overall construction quality.
It require less formwork compared to other slab systems, such as beam and slab or ribbed slabs. This leads to cost savings and reduced construction time, as less material and labor are needed for formwork assembly and removal.
Capability to Carry Concentrated Loads
Flat slabs have the ability to carry concentrated loads effectively. The absence of beams or ribs allows for more direct load transfer from the slab to the columns, making flat slabs suitable for areas with heavy point loads or equipment.
Reduction in Overall Height of the Structure
It help reduce the overall height of the structure. The absence of beams or drop panels allows for a thinner slab thickness, resulting in a lower overall building height. This can be advantageous in projects with height restrictions or where a compact design is desired.
It generally provides better fire resistance compared to other floor systems. The absence of beams or ribs reduces the potential for fire propagation and allows for more effective fireproofing measures, enhancing the overall fire safety of the structure.
Improved Appearance and Light Diffusion
It offer better appearance and diffusion of light. The absence of beams or drop panels creates a clean and uncluttered look, allowing for more design flexibility and the potential for larger uninterrupted spaces with ample natural light.
It can reduce moments (bending forces) in the slab by reducing the clear or effective span. This can lead to a more efficient and economical design, as it allows for a reduction in the required slab thickness or reinforcement. Additionally, reducing slab moments can improve the overall performance of the structure by minimizing deflections and vibrations.
Disadvantages of Flat Slab
It typically require a higher slab thickness compared to other slab systems, such as beam and slab or ribbed slabs. This is due to the absence of beams or ribs that provide additional stiffness and load distribution. The increased slab thickness can result in additional material and construction costs.
Not Suitable for Masonry Partitions
It may not be suitable for supporting masonry partitions directly. The absence of beams or ribs can make it challenging to provide adequate support for the weight of masonry walls. Additional measures, such as using load-bearing walls or providing additional structural elements, may be required to support masonry partitions in flat slab structures.
Flat slabs have limitations when it comes to accommodating larger spans. The absence of beams or ribs reduces the structural efficiency and load-carrying capacity of the slab. As a result, flat slabs may not be suitable for projects that require long spans without additional support or where larger column-free spaces are desired.







